Pennsylvania
From Wikimarcellus
Gas exploration, drilling and production is well under way in parts of Northeast, Central and Southwest Pennsylvania, along the line by which the Appalachian ridges diagonally cut across the state.
Areas in northcentral and northeastern Pennsylvania that have never before seen very much gas well drilling are expected to be especially prospective for Marcellus shale. It underlies approximately two-thirds of the state.
Drilling hotspots include the rural counties of Bradford, Lackawanna, Susquehanna, Wayne and Wyoming in the northeastern part of the State, Westmoreland in the west, and Greene and Washington Counties in the southwest.
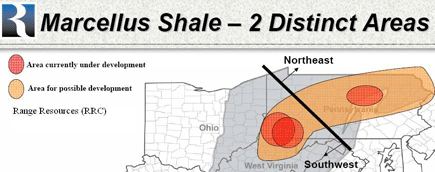
Pennsylvania hot spots are in orange—other prospective areas in beige.
Courtesy of Range Resources[1]
According to one estimate, by 2008, natural gas exploration companies have already spent roughly $2 billion for drilling rights in the State, seismic testing, and other tasks in pursuit of Marcellus shale gas.
Since 2005, over 500 drilling permits have been approved for drilling operations in the Marcellus shale areas of Pennsylvania. At least half of these were issued during 2008 representing a groundswell of interest in drilling this formation. A later report dated January, 2009 indicated that permits for 792 wells prospective for Marcellus shale have been issued in Pennsylvania. 571 permits were for vertical wells and 221 horizontal. In order to provide some background, in 2008 a total of 7,924 permits were issued for all types of wells including those that happened to be Marcellus shale, and of those, roughly 4,200 ended up finally being drilled.
According to an October, 2008 report, Marcellus shale drilling was taking place on roughly 275 well sites in the State, but at that time fewer than 20 wells were actually producing gas.
Another October report stated that the shale formation is at its thickest in Bradford County, Pennsylvania. 3,644 new leases for drilling rights were recorded there during the first nine months of 2008. Bradford County is where Pennsylvania's oil boom of the 1860s first began.
As of 2008, most gas pipeline infrastructure is located primarily in Southwestern Pennsylvania. Central and Northeastern Pennsylvania have very little infrastructure since most drilling has been comparatively recent in these parts of the State, and there has been little need for it.
Pennsylvania is strategically located to become a focus of natural gas production in the U.S. with sixty percent of the population of the country located within 300 miles. That makes it one of the best places in the world to sell natural gas, and companies producing in Pennsylvania can expect to command a premium price.

